Immersive Skills Development: Implementing VR Training for Critical Competencies
Building High-Value Skills Through Virtual Reality Experiences
When Jennifer, an HR director at a global logistics firm, first heard about virtual reality (VR) training, she was skeptical. Could employees really learn to drive delivery trucks or handle difficult customer conversations by donning a headset and stepping into a simulated world? Yet, as her company’s skills-first management journey matured, she found herself searching for ways to accelerate critical skill development, improve retention, and make learning more engaging. Like many forward-thinking organizations, Jennifer soon discovered that VR training isn’t just a technological novelty- it has evolved from an experimental technology to a transformative force in corporate learning environments.
Strategic Applications of VR in Skills-First Organizations
The shift toward skills-first management compels organizations to focus on the competencies that most directly impact business performance. The question for HR leaders is: which skills are best developed through immersive experiences? The answer, increasingly, lies in those competencies that benefit from situational practice, emotional engagement, and hands-on execution in environments that would otherwise be impractical to recreate.
Technical skills benefit tremendously from VR implementation, particularly those involving:
Equipment operation and maintenance in manufacturing settings
Procedural workflows requiring precise execution
Spatial awareness and physical manipulation tasks
Emergency response protocols and safety procedures
However, VR's most transformative impact may be in power skills development, where traditional training methods often fall short.
Skills particularly suited for VR development include:
Customer service interactions and conflict resolution
Leadership and difficult conversations
Empathy and diversity awareness
Public speaking and presentation skills
For example, at UPS, VR has revolutionized driver safety training. Instead of passively watching videos or reading manuals, trainees now step into a virtual world where they must identify hazards, react to unpredictable road conditions, and make split-second decisions- all from the safety of a training room. The result? A 75% reduction in training time, with no loss in effectiveness. This is just one illustration of how VR excels at developing technical skills that require muscle memory and situational awareness.
VR's Unique Advantages for Skills Acquisition
Unlike traditional training approaches, VR creates embodied learning experiences that engage multiple senses simultaneously. This offers several distinctive advantages:
Experiential practice: VR enables learning by doing in realistic environments without real-world consequences. Trainees can practice complex procedures or challenging scenarios repeatedly until mastery.
Safe failure environments: Employees can experiment with different approaches without risk, making VR ideal for training in hazardous situations or high-stakes customer interactions.
Enhanced focus: Research shows VR learners are distracted less frequently and can refocus themselves faster than those in traditional learning environments.
Emotional engagement: VR creates authentic emotional responses that mirror real-world situations, making it particularly effective for developing empathy and interpersonal skills.
At Verizon, call center employees use VR to practice handling difficult customer interactions. The immersive environment allows them to rehearse responses, manage their emotions, and build empathy, all while receiving immediate feedback. Neuroscientific research supports these outcomes: VR’s multisensory engagement activates multiple neural pathways, deepens emotional memory, and significantly improves knowledge retention compared to traditional methods.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of VR vs. Traditional Training
Of course, investing in VR must be grounded in a clear-eyed cost-benefit analysis. While initial implementation costs are higher than traditional training methods, these costs drop dramatically over time, especially when training is scaled across multiple cycles and locations. UPS, for example, calculated that their VR driver training program not only reduced training time by 75% but also reduced travel and facility expenses, making the business case for VR compelling.
Building the Business Case for VR Training Investment
A compelling business case for VR training should address:
Skills criticality assessment: Identify which skills most directly impact business outcomes
Current training gaps: Document limitations in existing training approaches
Implementation costs: Hardware, content development, infrastructure, and support
Projected savings: Reduced training time, travel expenses, and instructor costs
Performance improvements: Anticipated productivity gains, safety improvements, and quality enhancements
Competitive advantage: Enhanced employee capabilities that differentiate your organization
VR Solution Selection Framework
Selecting the right VR solution requires a nuanced understanding of both the technology and the organization’s skills development needs. Jennifer’s team, for instance, began by mapping out which competencies were most critical for their logistics operations- hazard recognition, equipment operation, and customer service. For each, they considered whether off-the-shelf VR content could meet their needs or if custom scenarios would be required to reflect their unique processes and equipment.
Hardware decisions followed. Tethered headsets offered higher fidelity and were ideal for detailed technical simulations, but their cost and setup requirements made them less practical for widespread deployment. On the other hand, standalone headsets provided portability and ease of use, making it feasible to bring VR training directly to distribution centers nationwide.
Budgeting for VR meant looking beyond initial hardware and software expenses. Jennifer’s finance partner helped her calculate the total cost of ownership, factoring in device management, content updates, technical support, and integrating VR with existing learning management systems. This holistic view ensured the investment would be sustainable as the program scaled.
Content Solutions: Off-the-Shelf vs. Custom Development
VR content must align closely with the work environment. Off-the-shelf training scenarios can be quickly and relatively cheaply used for many roles. For other roles, custom VR content is necessary.
Off-the-shelf VR content:
Lower initial investment
Faster implementation timeline
Standard metrics and analytics
Addresses common training scenarios like customer service, safety, and compliance
Limited customization to organizational specifics
Custom VR development:
Tailored to specific organizational environments and processes
Precise alignment with internal competency frameworks
Can incorporate proprietary equipment or procedures
Higher development costs (personnel costs typically account for 87.7% of custom development budgets)
Longer implementation timeline
Many organizations benefit from a hybrid approach, using off-the-shelf solutions for general skills while developing custom content for organization-specific competencies.
Implementation Planning and Execution
Rolling out VR training in a large organization is a journey, not a single event. Jennifer’s team began with a technical infrastructure assessment, ensuring that their network could handle the bandwidth demands of VR content and that physical spaces were available for safe, distraction-free use. Device management systems were implemented to track headsets, push updates, and monitor usage.
A phased implementation roadmap guided the rollout. The first phase focused on a pilot program with a select group of drivers and customer service representatives. Feedback loops were established through surveys and interviews, allowing the team to refine scenarios and address usability issues. Facilitators received hands-on training, not only in technical troubleshooting but also in guiding learners through immersive experiences and interpreting performance data.
Change management proved critical. Some employees were initially hesitant, worried about motion sickness or unfamiliar technology. Jennifer addressed these concerns through transparent communication, leadership endorsement, and early success stories. As employees began to see the benefits- faster skill acquisition, more engaging learning, and improved performance- enthusiasm grew.
Technical Infrastructure Assessment and Preparation
Before VR deployment, organizations should evaluate:
Network capacity: Ensure sufficient bandwidth for content downloads and updates
Physical space requirements: Dedicated areas for safe VR usage
Storage and charging solutions: Secure locations for equipment maintenance
Device management systems: Software for monitoring, updating, and tracking usage
Integration capabilities: Connections to existing learning management systems
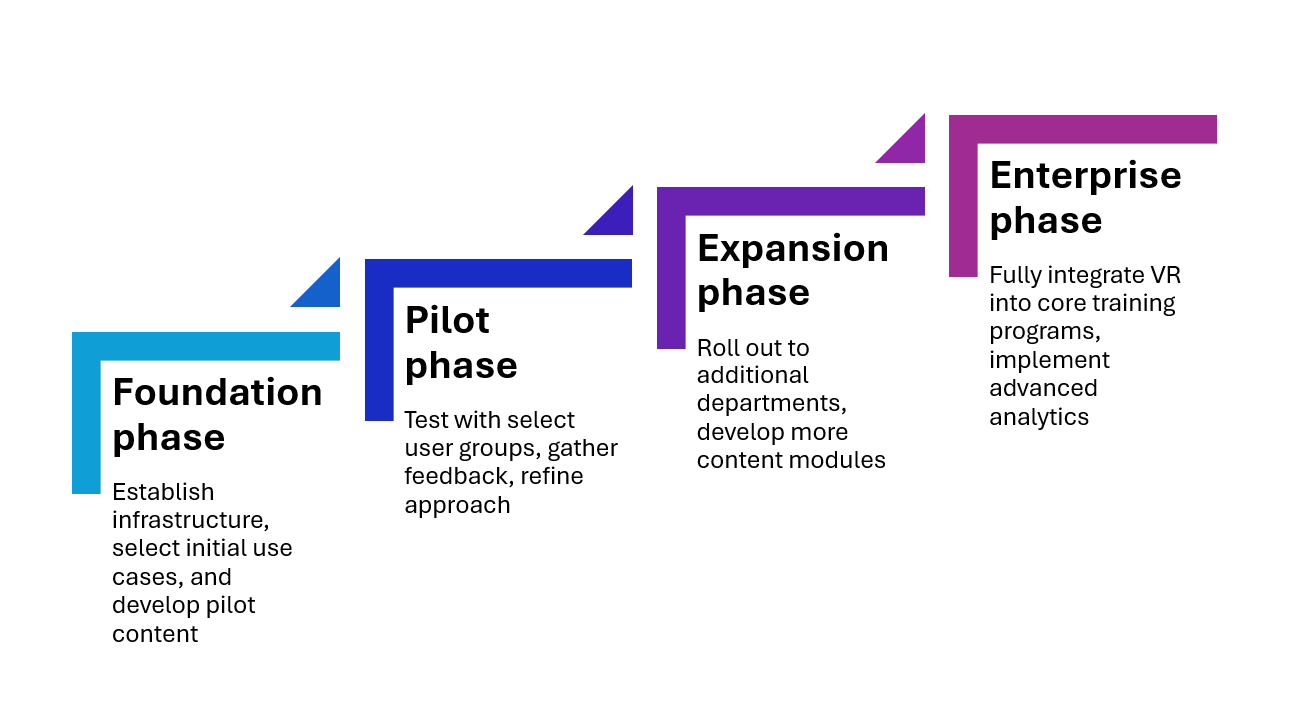
Developing a Phased Implementation Roadmap
Successful VR implementations typically follow a graduated approach:
Pilot Testing Methodology and Feedback Loops
Effective pilots require:
Clear success metrics aligned with training objectives
Diverse participant selection across roles and experience levels
Structured feedback collection through surveys, interviews, and observation
Performance comparison with traditional training methods
Iterative content refinement based on user experience
Training Facilitators and Technical Support Staff
Create robust training for those who will support the VR implementation:
Technical troubleshooting and basic maintenance procedures
Facilitation techniques for guiding learners through VR experiences
Data interpretation for performance assessment
Content customization capabilities for scenario adjustment
Change Management Strategies for Technology Adoption
Overcome resistance through:
Executive sponsorship and visible leadership participation
Early involvement of influential team members as champions
Clear communication about benefits and expectations
Addressing physical comfort concerns and accessibility needs
Celebrating and sharing early successes and improvements
Designing Effective VR Learning Experiences
The heart of VR training lies in the design of the learning experience. Effective scenarios are not just visually impressive; they are tightly aligned with the organization’s competency frameworks and learning objectives. At Volkswagen Group, for example, VR simulations take assembly workers inside a virtual engine, allowing them to practice procedures repeatedly until mastery is achieved. The scenarios are progressive, starting with basic tasks and building toward complex, real-world challenges.
Assessment is embedded within the VR environment. Learners receive immediate feedback on their actions, whether it is the proper placement of a part or the tone of voice used in a customer interaction. Eye tracking and behavioral analytics provide additional insight, allowing facilitators to identify where attention lapses or errors occur.
Importantly, realism is balanced with instructional design. While high-fidelity environments enhance immersion, the focus remains on learning outcomes. For instance, in Verizon’s customer service training, the avatars’ responses are carefully scripted to reflect real customer emotions. However, the scenarios are structured to ensure that key skills, such as de-escalation and empathy, are practiced and assessed.
Accessibility and inclusion are also prioritized. VR scenarios are designed to accommodate diverse learner needs, with adjustable settings for comfort, alternative input methods, and culturally sensitive content.
Integration with Broader Skills Development Programs
VR training is most powerful when integrated into a holistic skills development strategy. Jennifer’s organization connected VR modules directly to their competency frameworks, ensuring that performance data from virtual scenarios fed into the company’s skills inventory. Pre-VR e-learning modules provided foundational knowledge, while post-VR group discussions reinforced lessons learned and encouraged reflection.
Credentialing was streamlined through digital badges awarded upon successful completion of VR scenarios, and managers were tasked with observing and verifying skill transfer in real-world situations. Ongoing analytics tracked completion rates, long-term retention, and application of skills.
Measuring Impact and ROI
Demonstrating the value of VR training requires robust measurement. Jennifer’s team defined clear success metrics: training completion rates, proficiency improvements, error reduction, and employee satisfaction. Surveys revealed that employees found VR training more engaging and effective than previous methods, with many requesting additional modules.
Knowledge retention was tested at intervals, showing significantly higher scores for VR-trained employees than those who received traditional instruction. In safety-critical roles, incident rates dropped, and compliance improved. The ROI for VR training was clear and compelling when all factors were considered, including time savings, reduced travel, and operational efficiencies.
Defining Success Metrics Specific to VR Skills Training
Key performance indicators should include:
Completion rates: Percentage of employees finishing VR training modules
Time efficiency: Training time compared to traditional methods
Proficiency achievement: Percentage reaching competency thresholds
Error reduction: Decrease in mistakes during task performance
Knowledge retention: Testing at intervals following training completion
Employee Engagement and Satisfaction Measurements
Assess the learner experience through:
Satisfaction surveys comparing VR to previous training methods
Voluntary usage statistics for optional practice sessions
Sentiment analysis of feedback comments
Requests for additional VR training opportunities
Social sharing and peer recommendations
Knowledge Retention and Skills Proficiency Improvements
Document learning effectiveness with:
Pre/post assessments of knowledge and skill levels
Performance comparisons with traditionally trained groups
Longitudinal testing to measure retention over time
Application assessments in authentic work situations
Manager evaluations of skill demonstration
Safety Incident Reduction and Compliance Metrics
For safety-focused implementations, track:
Reduction in workplace accidents and near-misses
Compliance violation decreases
Proper procedure adoption rates
Emergency response effectiveness
Safety audit performance improvements
Calculating Comprehensive ROI Beyond Direct Training Costs
A thorough ROI analysis includes:
Training time reduction valued at the employee’s hourly costs
Decreased travel and facility expenses
Reduced incidents and associated costs
Productivity improvements from faster skill acquisition
Customer satisfaction increases and associated revenue impacts
While initial VR training implementation may appear more expensive, the ROI often becomes compelling when extrapolated over multiple training cycles and accounting for organizational scale.
Case Studies: VR Implementation Success Stories
Leading organizations across industries mirrored Jennifer’s experience. At UPS, VR training for drivers and package handlers not only reduced training time but also improved hazard recognition and operational consistency. Volkswagen Group’s use of VR for assembly and logistics training standardized procedures across global facilities and accelerated onboarding for new employees.
Verizon’s customer service VR program led to measurable improvements in empathy, calmness, and verbal fluency, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and reduced call escalation rates. In manufacturing, VR simulations for equipment operation and maintenance reduced errors and equipment damage, while in healthcare, VR-trained surgeons made fewer mistakes and demonstrated higher procedural proficiency.
Conclusion
The Transformational Power of VR for Skills-First Organizations
The journey to skills-first management is about more than adopting new technologies- it’s about reimagining how employees learn, grow, and contribute to organizational success. As Jennifer and her peers have discovered, virtual reality training offers a uniquely powerful way to build high-value skills at scale. It accelerates learning, deepens retention, and creates safe environments for practice and growth.
The evidence for HR leaders and executives is clear: VR training delivers measurable results, from faster onboarding and improved safety to enhanced customer service and technical mastery. As the technology continues to mature, the question is not whether to adopt VR, but how to integrate it most effectively into your broader talent strategy.
By embracing immersive learning, organizations can ensure that their workforce is not only prepared for today’s challenges but also equipped to thrive in the dynamic, skills-driven future of work.
Notes
https://www.strivr.com/blog/8-vr-training-benefits
https://ohsonline.com/articles/2023/03/17/benefits-of-vr.aspx
https://iq3connect.com/use-cases/technical-skills/
https://www.hurix.com/blogs/the-influence-of-immersive-learning-on-knowledge-retention/
https://arborxr.com/blog/customer-story-how-ups-saves-training-time-and-labor-costs-with-vr
https://www.talespin.com/reading/virtual-reality-manufacturing-training-use-cases
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1422600/
https://www.accenture.com/us-en/case-studies/technology/virtual-reality-ppe
https://zilliz.com/ai-faq/what-are-the-differences-between-tethered-and-standalone-vr-headsets
https://www.strivr.com/blog/off-shelf-vr-future-efficient-training
https://www.strivr.com/blog/vr-training-cost-analysis-and-true-roi
https://www.talentquest.com/immersive-learning/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7231540/
https://forwork.meta.com/au/vr-learning-training/
https://www.viar360.com/how-virtual-reality-is-changing-ups-employee-training/
https://www.learningguild.com/articles/the-human-skills-challenge-using-xr-to-boost-soft-skills/
https://knowledgeanywhere.com/articles/virtual-reality-training-real-world-case-studies/
https://www.aacsb.edu/insights/articles/2023/03/vr-takes-soft-skills-training-to-the-next-level
https://virtualspeech.com/blog/vr-training-case-studies
https://virtualspeech.com