Improving Skill Visibility for Effective Skills-First Implementation
Overcoming Skills-First Implementation Challenges – Part 2
A critical challenge in skills-first transformations is gaining real-time visibility into workforce capabilities. While 74% of organizations recognize skills visibility as crucial for future success, only 14% can accurately inventory their employees' competencies. This gap creates significant barriers to talent optimization, internal mobility, and strategic workforce planning.
Clear visibility into workforce capabilities enables better decision-making, enhances talent mobility, and supports strategic workforce planning. By implementing robust systems to illuminate hidden skills, organizations unlock agility, reduce talent acquisition costs by up to 30%, and accelerate innovation through better capability alignment. This article explores key strategies for improving skill visibility across your organization.
The Visibility Imperative in Skills-First Organizations
Modern enterprises operate with increasingly fluid talent requirements – 58% of workforce skills are repurposed annually across industries. Traditional static HR systems fail to capture this dynamism, leading to $8.5 trillion in lost productivity from skill underutilization, according to the World Economic Forum’s research.
Skills visibility enables organizations to:
Match emerging business needs with existing capabilities
Identify skill adjacencies for internal mobility
Surface hidden expertise for project staffing
Prioritize targeted upskilling investments
Building a Centralized Skills Inventory Hub
A centralized skills inventory acts as the organizational "nervous system," providing a real-time, comprehensive view of workforce capabilities and enabling informed decision-making. This requires a common skills vocabulary or taxonomy, data integrated across the enterprise into a centralized repository or database, and analytical capabilities to identify skills gaps, identify skills needs trends, and conduct workforce planning.
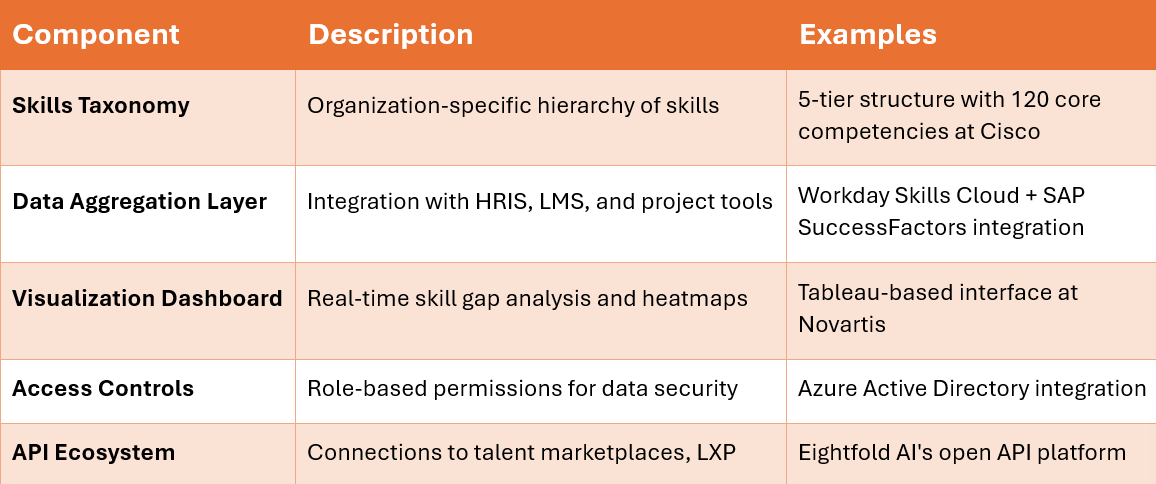
Key Components of an Effective Skills Inventory Hub
Phased Implementation
EPAM Systems demonstrates this approach through their Skills Ontology Platform, which reduced project staffing time by 40% by mapping 57,000 employees' capabilities against 2,100 defined skills.
Leveraging Technology Platforms for Dynamic Skill Management
Modern technology platforms are crucial in managing and visualizing skills data effectively. Several leading platforms offer comprehensive solutions for skills management:
Platform Capability Table
Implementation Best Practices
Platform Selection
Assess organizational needs and capabilities
Evaluate integration requirements
Consider scalability and future needs
Data Migration
Ensure data quality and consistency
Implement data governance protocols
Maintain regular updates and maintenance
Ideas to consider
Start with skills inference engines to populate initial inventories (85% accuracy in the latest AI models)
Use blockchain-based verification for critical technical skills (implemented by Siemens for engineering roles)
Enable employee-curated skill profiles with manager validation (Adobe's Model)
Novartis achieved 92% skills coverage in 18 months through Workday Skills Cloud, integrating data from 14 legacy systems.
Activating Internal Talent Marketplaces
Internal talent marketplaces increase skills visibility by 73% while reducing external hiring costs by 34% (Deloitte). These platforms connect employees with short-term projects, stretch assignments, and new roles based on their skills and career aspirations.
Key features of successful talent marketplaces include:
AI-powered matching algorithms to align employee skills with opportunities
Transparent opportunity postings across the organization
Integration with learning and development platforms for targeted upskilling
Analytics dashboards for workforce planning and skill gap analysis
HSBC, one of the world’s largest banking and financial services organizations, implemented a talent marketplace to drive internal mobility and provide workforce intelligence for strategic planning. The platform offers insights into skill distribution and employee career goals, enabling more informed decision-making.
Success Factors from Real World Examples:
Transparent opportunity postings (IBM's internal gig platform)
Skill-based matching algorithms (Unilever's Flex Experiences)
Participation incentives (Schneider Electric's digital badges)
Manager enablement tools (Siemens' Team Capacity Planner)
Cisco's internal marketplace reduced external tech hiring by 28% through better skills visibility across more than 50 countries.
Conducting Strategic Skills Mapping
Regular skills mapping, or better yet, continuous skills mapping, ensures that organizations maintain an accurate understanding of their workforce capabilities and can adapt to changing needs. Implement a four-layer mapping process:
Four-Layer Mapping Process
Strategic Layer: Link skills to 3-year business objectives
Workforce Layer: Map current skills against future needs
Process Layer: Identify skill-enabled process improvements
Individual Layer: Create personalized development paths
Utilize AI-powered job architecture analysis and real-time skills gap detection tools to support this process. Rolls-Royce conducts quarterly skills mapping sessions across engineering teams, reducing critical skill shortages by 63% in 24 months.
Creating Centralized Skills Data Hubs
Centralized skills data hubs serve as the foundation for improved skill visibility. These hubs aggregate data from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive view of the organization's skill landscape.
Key considerations for creating effective skills data hubs:
Data Integration: Implement robust Extract, Transform, & Load (ETL) processes to consolidate data from various HR systems, learning platforms, and project management tools.
Data Quality Management: Establish data cleansing and validation processes to ensure accuracy and reliability of skills data.
Skills Ontology: Develop a standardized skills taxonomy that aligns with industry standards and organizational needs.
Real-time Updates: Implement mechanisms for continuous data refresh to maintain an up-to-date skills inventory.
Analytics and Reporting: Integrate advanced analytics capabilities to derive actionable insights from skills data.
User Interface: Design intuitive dashboards and search functionalities for easy access to skills information.
Measuring Visibility Impact
Conclusion
Superior skills visibility transforms talent from an abstract concept to a strategic asset. Organizations can better understand and utilize their workforce capabilities by implementing centralized skills hubs, leveraging advanced technology platforms, promoting internal talent marketplaces, and conducting regular skills mapping exercises. This enhanced visibility leads to improved decision-making, increased organizational agility, and better talent outcomes.
The journey to improved skill visibility requires sustained commitment and investment, but the benefits - including enhanced workforce planning, improved talent mobility, and better organizational performance - make it worthwhile for organizations committed to skills-first talent management. The following article in this series will address managing complexity in skills data collection, exploring advanced governance models, AI-driven analytics, and cross-system integration strategies to maintain visibility at scale.
Notes:
https://www.imocha.io/blog/talent-visibility
https://www.avature.net/blogs/the-talent-marketplace-a-comprehensive-guide/
https://eightfold.ai/blog/talent-marketplace-explained/
https://www.kohezion.com/blog/data-centralization
https://gloat.com/blog/internal-talent-marketplace-implementation/
https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/how-to-start-smart-with-a-talent-marketplace/
https://hevodata.com/learn/data-centralization/
https://gloat.com/blog/opportunity-hub-skills-based-organization/
https://hbr.org/2023/05/how-to-design-an-internal-talent-marketplace
https://blog.workday.com/en-ca/talent-marketplace-foster-internal-mobility-3-ways-know.html
https://gloat.com/blog/talent-marketplace-implementation/
https://www.torryharris.com/insights/articles/global-capability-centers-as-data-hubs
https://blog.aspiresys.com/integration/6-best-practices-for-centralized-data-strategy/
https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/topics/talent/organizational-skill-based-hiring.html
https://www.selecthub.com/talent-management-system/eightfold-vs-workday-talent-management
https://blog.degreed.com/new-degreed-workday-partnership-more-skill-data-for-smarter-l